How Does Tooth Decay Happen? The Shocking Truth Revealed!

Tooth decay occurs when harmful bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the tooth enamel. These acids break down the sugars and carbohydrates in food, forming plaque, which coats the teeth and leads to decay.
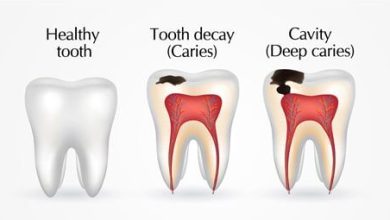
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common oral health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It happens when the bacteria present in the mouth interact with the sugars and starches from the food we eat. These bacteria produce acids that attack the outer layer of the teeth, known as the enamel.
Over time, the acids break down the enamel, forming tiny holes or cavities. If left untreated, tooth decay can progress and reach the deeper layers of the tooth, causing pain, infection, and even tooth loss. Therefore, understanding the causes and preventive measures to combat tooth decay is crucial for maintaining good oral health.

Credit: www.ancient-origins.net
The Causes Of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay occurs when the protective enamel on our teeth begins to break down, leading to the formation of cavities. There are several causes of tooth decay that can contribute to this process.
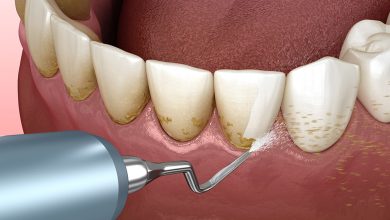
| Poor oral hygiene practices | Neglecting to brush and floss regularly allows plaque to build up on the teeth, which can lead to tooth decay. |
| Consumption of sugary and acidic foods | Eating foods and drinks that are high in sugar and acids can contribute to tooth decay by providing an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive. |
| Bacterial presence in the mouth | Our mouths naturally contain bacteria, some of which are harmful and produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to decay. |
Maintaining a good oral hygiene routine, avoiding excessive sugar and acid intake, and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups are all important factors in preventing tooth decay.
The Stages Of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common oral health issue that affects people of all ages. It occurs when the bacteria in our mouth produce acids that erode the protective layer of our teeth, known as enamel. The process of tooth decay can be divided into several stages, each with its own characteristics:
| Stages of Tooth Decay |
|---|
| Formation of plaque: Plaque is a sticky film that forms on the surface of our teeth. It consists of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. When we consume sugary or starchy foods, the bacteria in plaque metabolize these substances and produce acids that attack the enamel. |
| Enamel demineralization: Over time, the acids from plaque begin to demineralize the enamel, causing it to weaken and lose its protective properties. This can result in the formation of tiny holes in the teeth, known as cavities. |
| Dentin decay: If left untreated, the decay can progress and reach the dentin, the layer underneath the enamel. Dentin is softer and more vulnerable to acid attacks. Once the decay reaches the dentin, it can spread faster and cause more extensive damage. |
| Pulp involvement: The innermost layer of our tooth, called the pulp, contains nerves and blood vessels. When the decay reaches the pulp, it can lead to severe pain, infection, and potential tooth loss. Treatment at this stage may require root canal therapy or extraction. |
To prevent tooth decay, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Additionally, reducing the consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks can significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay.
Common Symptoms Of Tooth Decay
|
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, occurs when the structure of a tooth is damaged due to acid produced by bacteria in the mouth. This acid gradually eats away at the enamel, causing cavities to form. It is important to be aware of the common symptoms of tooth decay to prevent further damage.
|
The Role Of Bacteria In Tooth Decay
The Role of Bacteria in Tooth Decay
Oral bacteria play a crucial role in the development of tooth decay. These microorganisms inhabit our mouths, forming biofilms on our teeth known as dental plaque. As these bacteria feed on carbohydrates from food and beverages, they produce acid as a byproduct. This acid demineralizes the outer layer of our teeth, known as enamel, creating an acidic environment that is conducive to the progress of tooth decay.
Over time, this acid attack weakens the enamel and leads to the erosion of tooth structures. The acid dissolves the minerals in the tooth, causing cavities to form. If left untreated, tooth decay can progress to deeper layers of the tooth, eventually reaching the nerves and causing severe pain and infection.
Preventive Measures For Tooth Decay
Tooth decay occurs when the enamel, the protective layer covering the teeth, breaks down due to bacterial activity. This can happen when we consume sugary and acidic foods, as these substances create an environment that promotes bacterial growth and plaque formation. Regular brushing and flossing are crucial preventive measures to remove plaque and inhibit bacteria. Brushing twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily help remove food particles and plaque from hard-to-reach areas, reducing the risk of tooth decay.
Limiting sugar and acidic food intake is also vital in preventing tooth decay. High-sugar and highly acidic foods and beverages contribute to the erosion of tooth enamel, making teeth more susceptible to decay. It is essential to opt for healthier alternatives and limit consumption of sugary treats and acidic drinks to maintain good oral health.
In addition to proper oral hygiene and a balanced diet, dental sealants and fluoride treatments are effective preventive measures against tooth decay. Dental sealants are a protective coating applied to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth, sealing off the deep grooves and preventing the accumulation of food debris and bacteria. Fluoride treatments help strengthen tooth enamel and make it more resistant to acid attacks. These treatments are often recommended by dentists to further protect against tooth decay.
Treatment Options For Tooth Decay
| How Does Tooth Decay Happen? |
| Treatment Options for Tooth Decay |
Tooth decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that attack the enamel of the teeth, causing it to break down. This breakdown leaves the underlying dentin exposed and susceptible to further decay. If left untreated, tooth decay can lead to pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for tooth decay:
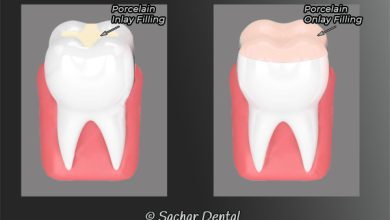
Dental fillings: Fillings are a common treatment for tooth decay. The decayed portion of the tooth is removed, and the space is filled with a material such as amalgam or composite resin.
Root canal therapy: When tooth decay reaches the pulp of the tooth, root canal therapy may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canal, and sealing it with a filling.
Dental crowns: Dental crowns are used when tooth decay is extensive and a filling is not sufficient. A crown is a tooth-shaped cap that is placed over the tooth to restore its shape, size, and strength.
Tooth extraction: In cases where tooth decay is severe and irreversible, tooth extraction may be recommended. This involves the removal of the decayed tooth, and it may be followed by tooth replacement options.
Complications Arising From Untreated Tooth Decay
Untreated tooth decay can lead to a variety of complications. One of the most common complications is gum disease, which occurs when the bacteria from the decay reaches the gums, causing inflammation and infection. This can result in redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding of the gums.
Another complication that may arise from untreated tooth decay is abscess formation. An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms in the tooth or the surrounding tissues. It can cause severe pain, swelling, and even fever. If left untreated, the infection from the abscess can spread to other parts of the body.
Tooth loss is yet another potential consequence of untreated tooth decay. As the decay progresses, it can weaken the tooth structure, leading to the tooth becoming loose and eventually falling out. This can impact a person’s ability to eat and speak properly and may require tooth replacement options like dental implants or bridges.
Additionally, untreated tooth decay can result in the spread of infection to the surrounding tissues. The bacteria from the decay can penetrate deeper into the tooth, reaching the pulp, and ultimately spreading to the bones and tissues supporting the tooth. This can cause severe pain, swelling, and further complications.
Promoting Oral Health And Preventing Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a common dental problem that occurs when the acids produced by bacteria in the mouth dissolve the protective layer of the teeth, known as the enamel. This process is known as demineralization and is caused by the consumption of sugary foods and drinks, poor oral hygiene, and a lack of regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
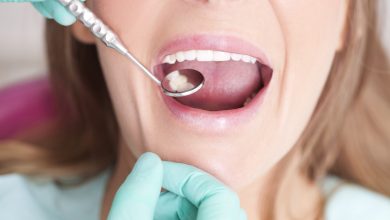
Promoting oral health and preventing tooth decay begins with regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Dentists can identify potential issues early on and provide necessary treatments or recommendations. Additionally, adopting a balanced diet is essential. Limiting the intake of sugary and acidic foods and drinks can help reduce the risk of tooth decay. Proper oral hygiene education and practices, such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily, are also essential to maintain good oral health and prevent tooth decay.
Frequently Asked Questions Of How Does Tooth Decay Happen?
What Is The Main Cause Of Tooth Decay?
Poor oral hygiene and excessive sugar consumption are the main causes of tooth decay.
What Are 5 Causes Of Tooth Decay?
Poor oral hygiene, such as infrequent brushing and flossing, increases the risk of tooth decay. Consuming sugary and acidic foods and drinks also contributes to decay. Tooth grinding and clenching, as well as dry mouth caused by certain medications, can weaken tooth enamel.
How Do I Stop My Teeth From Decaying?
To prevent teeth decay, follow these steps: 1. Brush your teeth twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste. 2. Floss once a day to remove plaque from between your teeth. 3. Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks in your diet.
4. Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. 5. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Can A Tooth Be Saved From Decay?
Yes, a decayed tooth can be saved through various dental treatments like fillings, root canal therapy, or dental crowns. These procedures help remove decay and restore the tooth’s structure, saving it from further damage or extraction. Regular dental check-ups can prevent decay and ensure early intervention if it occurs.
Conclusion
Tooth decay is a common dental issue that occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel. Maintaining good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly and having regular dental check-ups, is crucial in preventing tooth decay.
By understanding the causes and risk factors of tooth decay, we can take proactive measures to protect our teeth and maintain a healthy smile. Remember, prevention is always better than cure!